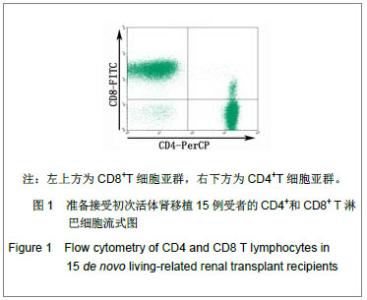
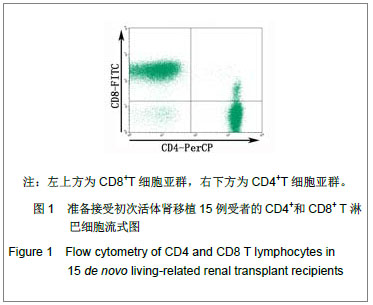
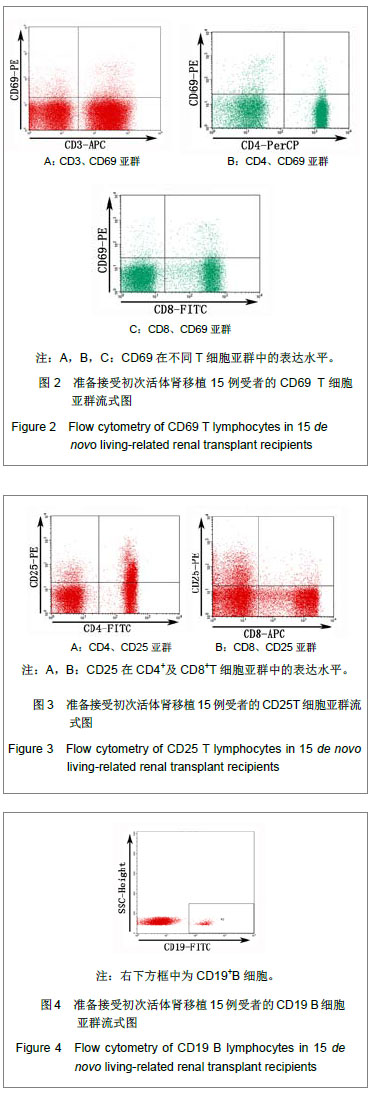
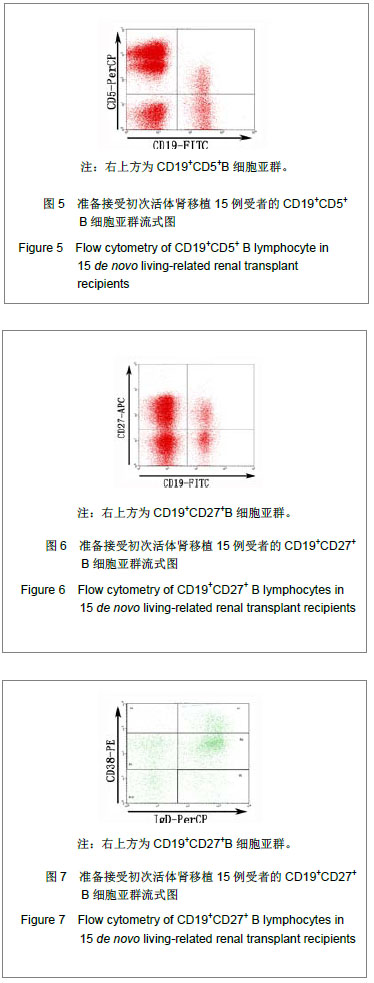
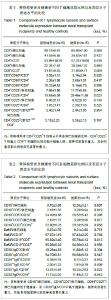
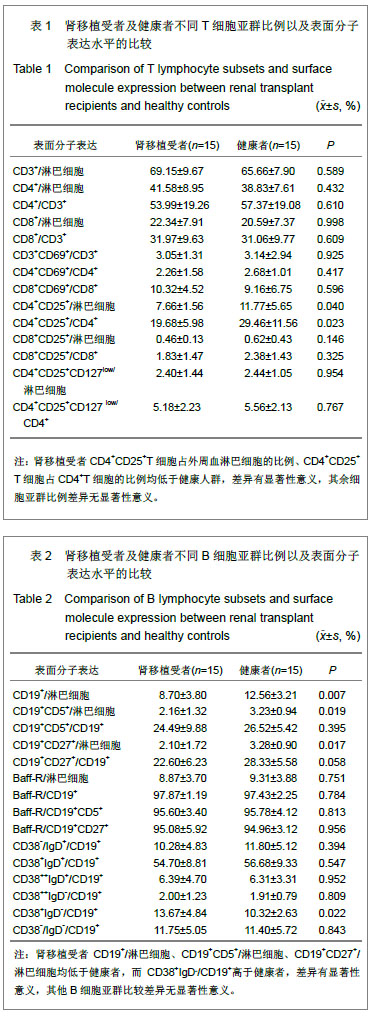
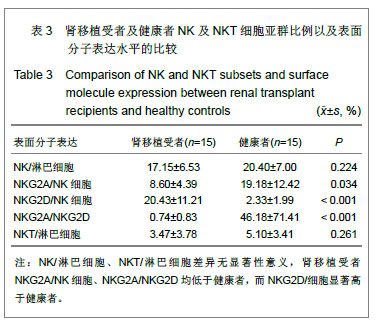
| [1] |
Yang Zhiwei, Liu Junchang, Gao Xiaolin, Jiang Taimao.
Relationship between tacrolimus metabolic rate and early BK virus infection after kidney transplantation
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 712-716.
|
| [2] |
Hu Mingzhi, Zhang Jingying, Yang Guoan, Pang Chunyan, Zhang Wei, Wang Yongfu, Sun Xiaolin.
Immunomodulatory effects of umbilical cord-mesenchymal stem cells modified by miR-1-5p on T lymphocyte subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4928-4938.
|
| [3] |
He Yixiang, Zhao Yuhao, Gao Zhao, Zhao Haiyan, Wang Wenji.
Effect of B lymphocytes and related cytokines on osteoclast differentiation in the osteoimmunology system
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(29): 4709-4714.
|
| [4] |
Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin.
Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942.
|
| [5] |
Wang Xiaobo, Wang Changan, Han Jianle, Yang Qingyan, Yang Shuaiping, Yang Junwei.
Influence of conversion from cyclosporine to tacrolimus on glucose metabolism and cardiovascular risk profiles in stable kidney transplant patients
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2236-2240.
|
| [6] |
Liu Junchang, Gao Xiaolin, Jiang Taimao.
Correlation of CY3A5 genetic polymorphism with concentration/dosage of tacrolimus and individualized administration of tacrolimus after kidney transplantation
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1740-1744.
|
| [7] |
Guo Juan, Zheng Shan, Xie Hui, Hu Yahui.
An analysis of pathogenic bacteria infection in 422 kidney transplant recipients
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5198-5202.
|
| [8] |
Liu Luhao, Fang Jiali, Zhang Lei, Li Guanghui, Xu Lu, Lai Xingqiang, Xiong Yunyi, Chen Rongxin, Ma Junjie, Chen Zheng.
Clinical assessment criteria of donor pancreas transplants for simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4157-4161.
|
| [9] |
Feng Yang, Yan Xu, Wang Yongkui, Yang Tengyue, Shang Lijie, Zhang Chunlin.
Relationship between degenerative lumbar disc disease and
peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(17): 2630-2635.
|
| [10] |
Zhao Xiao1, Zhang Fengbo2, Wang Hongying1, Yan Fang3, An Mengting1, Li Yujiao1, Pang Nannan4, Ding Jianbing1.
Dominant T cell and B cell epitopes in EgA31 protein of Echinococcus granulosus by bioinformatics
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1078-1083.
|
| [11] |
Lin Min, Wei Weili, He Yimi, Chen Zhikui.
Construction of a gene-loaded multifunctional polymer microbubble targeting breast cancer cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(34): 5468-5472.
|
| [12] |
Ma Chen, Li Xiaoguo, Xu Mingjun, Ma Xiaona, Ma Xiaowei.
Amplification and identification of human placental mesenchymal stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(33): 5293-5299.
|
| [13] |
Wang Jing, Cai Xia, Wang Zhiguo, Xu Quanchen, Li Kun, Hua Cheng.
Isolation and identification of exosomes from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2651-2658.
|
| [14] |
Yang Jin, Zhang Meixia, Yan Pei, Cheng Qiao, Li Jianzhen .
Meta-analysis of risk factors for new-onset diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2450-2460.
|
| [15] |
Xu Xiaoling, Pan Wangping, Lü Xiaojun, Zhang Ju, Hu Yuanhua, He Kaiyong.
Immunotoxicity of absorbable silk fibroin biofilm on rats
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2190-2195.
|